
Usually this area is quite large (8-20 GB).
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/005_how-to-check-free-hard-drive-space-in-windows-2619187-5beb61d6c9e77c0051cdfd2e.jpg)
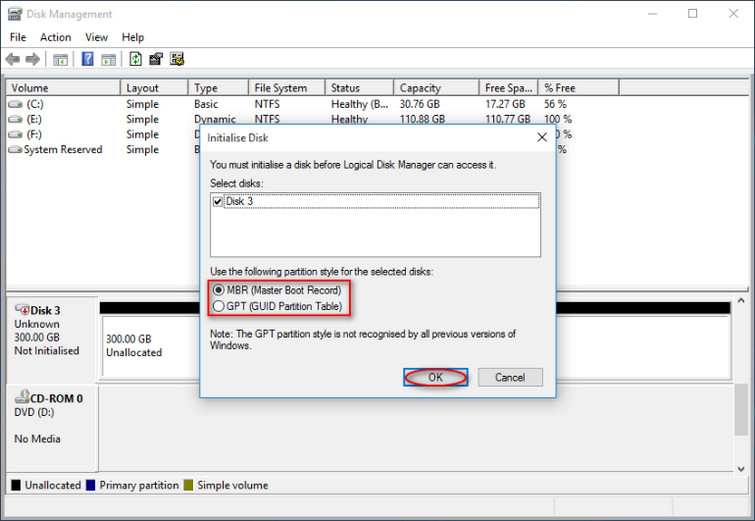
This area is used when you want to restore the original state of your desktop PC or laptop without using CD/DVD disks. Manufacturer of your PC can create a “Host protected area” on your hard drive to store an image of the original operating system and programs. Usually this area is not bigger than 10 megabytes, so there is nothing to worry about. Motherboard can create a so-called “Host protected area” on your hard drive to store its data. One decimal gigabyte contains 1 000 000 000 bytes (1000 x 1000 x 1000), whereas one binary gigabyte contains 1 073 741 824 bytes (1024 x 1024 x 1024) - that’s more than a 7% difference! So, your 300 GB hard drive will show up in Windows as a 279 GB hard drive. Hard drive manufacturers use decimal gigabytes while operating systems use binary gigabytes. Windows Vista does not have any issue with big drives. Windows 2000, 2003 and XP do not support big drives by default you will have to install the latest service pack in order to get big drives working properly on these OS. There are ways to get around this problem, but since these Operating Systems are rather rare nowadays, I do not see the point of writing about them. Windows 95, Windows 98 and Windows ME will not support big drives (>137GB) even if you install all hotfixes. Operating System does not support LBA-48 addressing mode Now I will go through these things one-by-one and provide some more details.
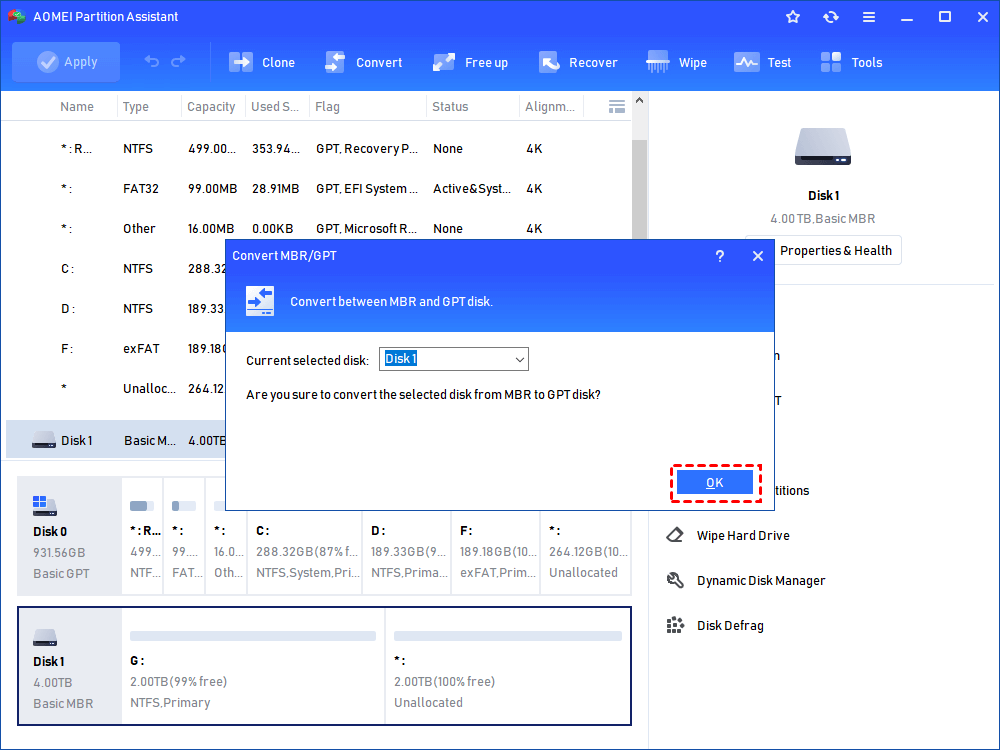
“My hard drive has mysteriously became smaller! How can I restore its full capacity?” At the end of this article there is a link to our program that recovers factory capacity of any hard drive. This article is a complete guide on recovering your hard drive’s factory capacity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
